Many recording artists and music producers often have doubts about what are the differences between an audio interface and a DAC unit. Even though both devices present some similarities, each of them serves a different purpose in the chain while listening and recording music.

Audio interfaces are an all-in-solution that you can use to plug in instruments and equipment such as guitars and microphones. Most interfaces have a built-in DAC. A DAC (short for digital to analog converter) is a device designed to convert the digital signal coming out of your computer and transform it into analog audio signals so that it can be translated to headphones and speakers.
Today, we will go through all the differences between audio interface vs DAC, and explain the particularities and applications of each one to help you decide the best option for your setup and workflow.
Tip: If you’re considering buying an audio interface and would like to know more about this type of product, please refer to our Best Audio Interface article.
Audio Interface vs DAC – Table Of Contents
- Audio Interface vs DAC – Differences
- What is a DAC and How Does It Work?
- Why Use DACs (Digital to Audio Converters)
- Problems a High Quality DAC Can Solve
- What is an Audio Interface and How Does It Work?
- Why Use Audio Interfaces
- Differences Between an Audio Interface and a DAC
- Bonus: What is a Headphone Amplifier?
- Best Models of Digital to Analog Converters
- Best Models of Audio Interfaces
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Final Verdict
Audio Interface vs DAC – Differences
The differences between an audio interface and a DAC might not seem like a lot but there are quite a few worth considering. A DAC, for example, is used to improve the quality of a device, including a smart TV, laptop, smartphone, etc. An audio interface, on the other hand, is a multipurpose device that allows you to record the audio, which a DAC can’t.
What is a DAC and How Does It Work?
DAC is short for digital to analog converter. The digital signal coming out of your computer or listening device can’t be promptly read by a pair of headphones or speakers, so the DAC will take care of turning this signal into an analog one. DACs are present in most devices in our daily lives: laptops, smartphones, etc.
To understand how a DAC works we need to recap the process of recording and storing sound. When we sing into a microphone, the device captures the sound waves in the form of an analog signal. If you’re recording it into a computer, your audio interface will take care of transforming it into a signal in the form of digital information/digital data that your computer can understand.
Finally, when you playback your recording, the DAC will process the signal invertedly. That is, make those digital signals analog once again.
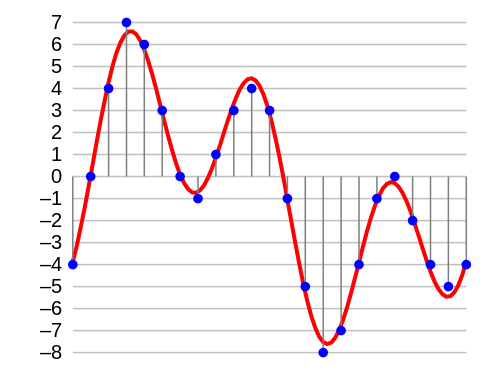
Representation of the audio signal. The red line is the analog wave signal and the blue dots are how it is converted into a digital signal. Source: Aquegg on Wikimedia Commons.
Digital signals are presented in the form of samples. These samples have different amplitudes along them that will vary according to the dynamic range of the audio file, which is called bit-depth.
On the other hand, audio as an analog signal is represented as an electrical pulse, which, unlike digital samples, is a steady and continuous wave.
To translate the analog signal wave into digital audio form, the DAC will create intersecting points according to the sample rate of the file (usually 44.1kHz or 48kHz). When transforming from digital to analog, it is the opposite.
Why Should I Use a DAC (Digital to Audio Converter)?
Now, you may be asking yourself: what are the benefits of using a standalone dedicated DAC if my device (computer, audio interface, etc.) already have one?
The problem is that the digital to analog converter found on most consumer-grade devices are usually of lower quality and intended for consumer use: with earbuds, low-powered speakers, etc. They may not be able to meet the standards and power required by professional-grade equipment such as high-impedance headphones and studio monitor.
Lower-quality DACs can also create audio artifacts such as jitter. A higher quality, external DAC can solve many of these problems, as we will see below.
Problems a High Quality DAC Can Solve
Jitter
Jitter is what happens when the device’s internal clock can’t keep in sync with the source of the digital signal, therefore creating timing problems and digital noises in the resulting analog signal.
Aliasing
Aliasing happens when the DAC can’t convert analog signals to be faithful to their digital sources. It usually causes a warbling effect in the audio and can impact the audio quality.
What is an Audio Interface?
If you’re into music production, you’ve probably come across audio interfaces in the past. These compact devices are made to simplify the process of recording professional audio and producing music in your home studio.
Audio interfaces usually feature one or more TRS inputs for plugging-in instruments such as guitars, basses, and keyboards in the form of a ¼ connector; And microphones with an XLR connector. These devices also feature a built-in DAC for translating your digital signal to the line and headphone outputs.
On most interfaces, these DACs have great sound quality, meaning you won’t have to invest in a standalone one. Also, unlike external converters, the ones present on these units are capable of both recording and audio playback.
Be aware that some cheap audio interfaces may have inferior quality DACs. We advise sticking with trustable, high-quality brands such as M-Audio, Apollo, Apogee, etc, and researching about the product before buying.
Why Should I Use an Audio Interface?
Audio interfaces are an all-in-one solution. They are the perfect choice if you want to record music without much hassle and in a cost-effective manner. Be sure to take into account some factors such as the number of audio inputs and outputs present in a unit and the quality of its components.
If you’re a home-studio-based music producer or a singer/songwriter, an audio interface with one or two XLR/Inst inputs will serve you well. You will be able to connect a microphone and instruments like guitar and bass to it.
For medium-sized to large-sized studios, you may need a larger number of connections in your audio interface. Also keep in mind that if you’re going to use a condenser microphone, you will need an interface with +48V phantom power to properly power your mic. Most devices nowadays come with this feature.
As said before, the DACs present on most of these audio interfaces have great sound quality, so you probably won’t need an external one. You may need, however, a headphone amp if you plan on using high-impedance headphones, such as the Beyerdynamic DT990 Pro, with an interface.
Differences Between an Audio Interface and a DAC
| Audio Interface | DAC (Digital to Audio Converter) | |
| Purpose | Recording and audio playback. | Audio playback. |
| Capabilities | Can convert analog signals into digital data and digital data into analog signals. | Can only convert digital signals into analog signals/analog audio. |
| Connectivity | Most audio interfaces will connect to your computer via USB or FireWire cable. | Bluetooth, USB, Optical |
| Inputs and Outputs | ¼ Instrument inputs, XLR inputs, and MIDI for recording. Line and headphone outputs for playback. | RCA, optical, and ¼ inch for headphones. |
| Power | Audio interfaces are usually powered by USB but some require an external power supply. | Usually powered by batteries or USB, in case you’re using it with a computer. |
| Portability | Will highly depend on the particular audio interface model. Some are more portable than others. | Most are usually portable and can be easily transported. |
Bonus: What is a Headphone Amplifier?
Some consumer-grade electronics and even audio interfaces may not be able to power higher-impedance headphones. In these cases, a standalone headphone amplifier is necessary to ensure better audio quality and maximum volume capability.
Some audio interfaces and DACs come with built-in headphone amps, so this will highly depend on the particular model of the unit. We recommend checking in the manufacturer’s specifications how many OHMs each device can power.
Best Models of Digital to Analog Converters
Below, we list two models of high fidelity DACs with different features and connections. The first is a great option for those who want a USB DAC with added Bluetooth compatibility, while the latter is a more affordable option.
Audioengine B1 Music Receiver – Best Bluetooth Option
The Audioengine B1 can connect to Bluetooth devices such as smartphones, laptops, and even smart TVs and audio system. The device is simple to pair and can also be connected via USB and RCA.
Product Specifications
- 24-bit Upsampled Playback
- Latency of ~30ms
- AKM AK4396 D/A Converter
- Included Cables
- Bluetooth, USB, and RCA Connection
CAMWAY Digital to Analog Converter – Best Budget Option
At $24,99 by the time this article was written, this DAC is a cheap option that will do the job if you’re on a budget. The product has received lots of positive feedback. One of the main features of this unit is the Bass Control. It is also a device capable of powering high-impedance headphones (up to 600 ohms, according to the manufacturer).
Product Specifications
- Coaxial Input
- Optical Input
- RCA Analog Outputs
- Headphone Output
- DC5V Powered
Best Models of Audio Interfaces
There are countless models of audio interfaces on the market. Varying across a wide price range, each one of them is more suitable for a particular use case. Below, we listed three options: budget, professional and compact.
Tip: The audio interfaces listed here can connect to your computer via USB, but there are also Thunderbolt options. If you want to learn more about this kind of interfaces, please read our Best Thunderbolt Audio Interfaces article.
M-Audio M-Track Duo – Best Budget Option
The M-Track Duo, by the well-renowned company M-Audio is a great option if you’re looking for your first audio interface. It has two combo XLR inputs for plugging in microphones and instruments via ¼ jack, as well as a high-quality built-in digital to analog converter and crystalline preamps.
Product Specifications
- 2 Combo XLR Inputs
- Stereo Line Outputs
- Headphone Output
- +48V Phantom Power
- USB Connection
Universal Audio Apollo Twin MkII – Best Professional Option
Universal Audio is one of the best audio interfaces manufacturers in the market. The Apollo Twin MKII features not only high-quality components but also DSP processing for audio effects and plugins based on faithful emulations of vintage gear such as compressors and equalizers. The unit has ultra-low latency.
Product Specifications
- 2 Combo XLR Inputs
- 2 Line Analog Outputs
- Stereo Line Outputs
- Built-In Preamps with Unison Capability
- DSP Processing
- Headphone Output
- +48V Phantom Power
- Optical Input
- USB Connection
Apogee One – Best Compact Option
The Apogee One is a good audio interface if you favor compact and portable audio devices. Despite its size, the One is capable of recording and playing back quality audio with low latency due to its top-notch components. One of the main differentials of this interface is the built-in microphone.
Product Specifications
- 1 XLR Input
- 1 Inst/Line Output
- Headphone Output
- 100% Compatible With Mobile Devices (Smartphones and Tablets)
- USB Connection
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is Sample Rate?
What Is Bit-Depth?
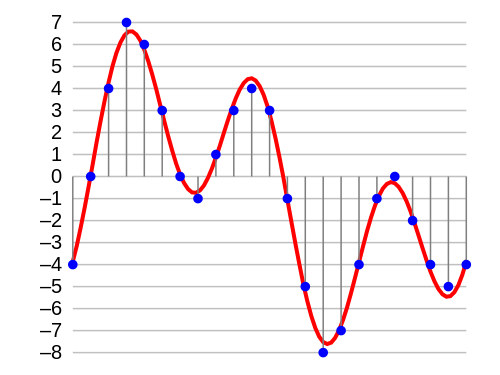
Source: Aquegg on Wikimedia Commons.
As discussed before, the red wave represents the analog audio signals. The blue dots that intersect represent samples of digital signals. Bit-depth means how high or low these samples can go, or how many possibilities they have in the conversion process. A smaller bit-depth may reduce the dynamic range of a song.
The most used bit-depths are 16, 24, and 32. However, there is barely an audible difference between them, if the bit-depth is at least 16 bits.
Will a Digital to Analog Converter Improve My Sound Quality?
Can I Use an Audio Interface Instead of a Digital to Analog Converter?
Can I Use a Digital to Analog Converter Instead of an Audio Interface?
Related: How to Connect a Mixer to an Audio Interface article.
Final Verdict
In this article, we’ve learned about the differences between an audio interface vs DAC (digital to analog converters). Basically, the best application for an audio interface is when you plan on recording music inside your computer and for music production. Most audio interfaces already come with a built-in DAC so there’s no need for a standalone one.
A standalone DAC is useful if you just want to improve the audio quality of a device such as a smartphone, a laptop, or a smart TV. A DAC is only capable of audio playback so you won’t be able to record audio with it (like in the case with an audio interface).
Remember to check the connection and compatibility of each device before you make any purchases. If you’re thinking about buying an audio interface, consider checking our related articles to aid you in your decision.We hope our audio interface vs DAC article was helpful. Please share this article with someone that you think would like to read it and don’t hesitate to contact us if you have any questions or want to discuss further about the subject!
Ian Sniesko is an experienced music producer and musician who loves to share his knowledge about the best audio equipment for making and enjoying great music. For the past 6 years, Ian has written extensively about the audio equipment industry and has contributed to many of the top music magazines.




